The AI Agent Business Model Will Replace SaaS
The Evolution from Traditional Software to SaaS, and Now to the AI Agent Business Model

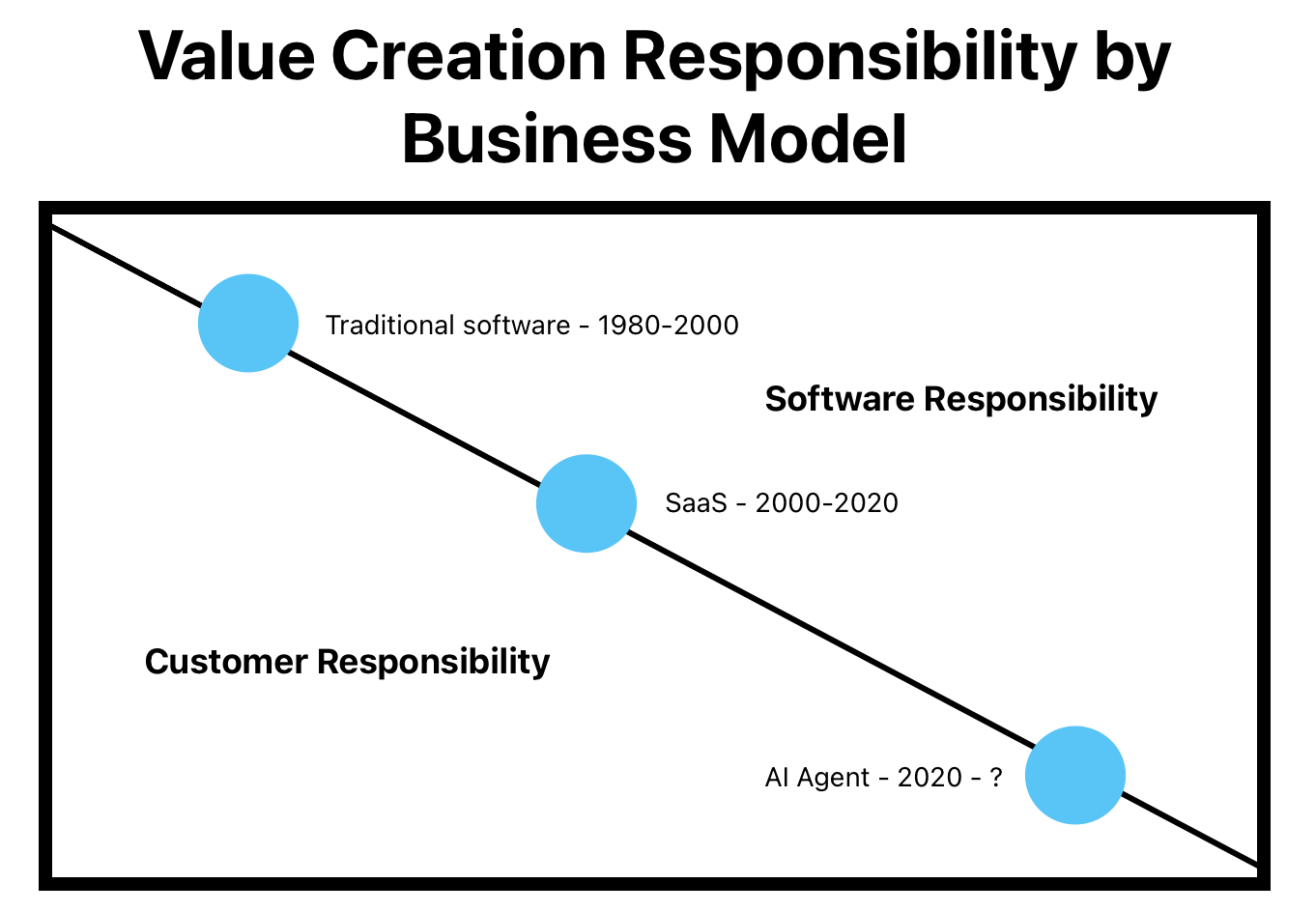
Software has always been about solving problems, but how it delivers value has evolved over time. From traditional software to SaaS and now AI Agents, each phase represents a shift in responsibility—moving progressively from the customer to the software.
At every step, customers do less while software takes on more. AI Agents represent the ultimate step in this evolution, fully automating outcomes and leaving almost nothing for the customer to manage.
1980–2000: Traditional Software — The Customer Does the Heavy Lifting
In the early days, software products were built to automate specific tasks but left the customer responsible for making them work.
What Customers Had to Manage
Setup and Customization: Implementations could take months to configure.
Operational Management: Customers were on the hook for updates, maintenance, and infrastructure.
Steep Learning Curve: Complex systems demanded significant training and upfront investment.
These solutions were rigid, expensive, and carried high risks, making them accessible only to larger businesses.
2000–2020: SaaS — Vendors Take on More Responsibility
SaaS changed everything by shifting much of the operational burden to vendors. Software moved to the cloud, making it easier to deploy, scale, and maintain.
How SaaS Reduced the Load
Simplified Onboarding: Faster setups, intuitive interfaces, and minimal configuration.
Managed Infrastructure: Vendors handled uptime, updates, and scaling.
Flexible Pricing: Subscription models allowed businesses to pay as they grew.
However, the customer still had work to do:
Decision-Making: They had to figure out how to use the software effectively.
Task Execution: SaaS provided tools, but results were still the customer’s responsibility.
SaaS made software more accessible, but it didn’t eliminate the need for human involvement or fully align incentives between businesses and software providers.
2020–2040: AI Agents - Full Outcomes from Software
AI Agents are the next big leap. Unlike traditional software or SaaS, these systems don’t just provide tools for users—they autonomously deliver results.
Execution, optimization, and outcomes are all handled by the software itself.
How AI Agents Take Ownership
Outcome Delivery: No features or dashboards—just results.
Zero Setup: No onboarding, no training, no configuration. Deployment happens instantly.
Self-Management: AI Agents run and optimize themselves with little to no oversight.
Continuous Improvement: They learn from their environment and get better over time.
For customers, the software becomes almost invisible. All that matters is the outcomes.
Why AI Agents Will Disrupt SaaS
Over the next 20 years, the AI Agent model will challenge and likely replace SaaS in many areas.
Here’s what sets AI Agents apart:
Outcome-Based Pricing: Customers pay for results, like a percentage of revenue generated or costs saved. This aligns costs directly with value.
Human-Like Interfaces: AI Agents interact like humans—via text, speech, or browser actions—removing the need for complex integrations or APIs.
Dynamic Decision-Making: AI Agents rely on real-time conversation streams (emails, messages, calls) rather than rigid relational data structures.
Massive Cost Savings: By automating repetitive tasks, AI Agents will disrupt labor-intensive processes, freeing up resources for higher-value work.
Winner-Takes-All Market: The best AI Agents will dominate, benefiting from superior data, rapid iteration, and self-reinforcing growth cycles.
How AI Agent Companies Will Win
Building AI Agent businesses won’t be easy. It requires deep expertise beyond just training AI models. Cloud providers will likely dominate the foundational AI layer, taking a cut of the revenue from businesses built on their platforms. The real value lies in domain-specific execution.
Key Success Factors
Access to Data: The more relevant data, the better the outcomes.
Seamless Integration: Plug into existing workflows without disruption.
Domain Expertise: Industry-specific prompts and validation mechanisms.
Human Oversight: To manage and refine AI at scale.
Scale: Larger datasets drive better AI performance and outcomes.
Similar to SaaS, AI Agent businesses will target specific niches but focus on automating repetitive workflows end-to-end.
Examples of AI Agent Niches
Customer service automation
Sales lead qualification
Accounts payable processing
Contract review and compliance
Vendor onboarding
Marketing asset personalization
How AI Agent Businesses Will Emerge
Delivering AI Agents businesses will be challenging and require significant expertise beyond foundational AI models, which are rapidly commoditizing. Cloud vendors are likely to dominate the foundational AI layer, taking a 10% revenue cut from businesses leveraging their models.
Vertical Specialization: Similar to SaaS, AI Agent businesses will target specific niches but focus on automating repetitive workflows end-to-end.
Potential Use Cases
Customer Support and Service Desk Automation
Sales Lead Qualification
Accounts Payable Processing
Contract Review and Compliance Checks
Expense Report Reconciliation
Vendor Onboarding
Marketing Asset Personalization
Keys to Winning in These Niches
Access to all relevant data.
Seamless integration with existing business applications.
Domain-specific prompting and validation.
Human oversight to manage AI at scale.
Scale within the domain—larger datasets yield better outcomes.
The Future: A Focus on Creativity and Connection
AI Agents will redefine how businesses operate, freeing them from mundane tasks and allowing them to focus on creativity, innovation, and human connection. The promise of software will finally be fulfilled—not as a tool we have to master, but as a partner that helps us reach our full potential.



I love seeing things in new ways—your timeline showing shift in customer/software responsibility resonates. And I love your declaration for a future with space to focus on creativity and connection.
Looking at history, I feel like a similar promise was held behind technical advances, only to backfire. E.g. the Industrial Revolution promised to cut physical labor and led to widespread worker exploitation and dangerous factory conditions. The computer and internet revolutions aimed to enable shorter work weeks with more leisure time and flexible work, yet most now work longer hours—always on call, 24/7 expected availability, and precarious gig worker conditions.
Given your deep insight into this transition, what role do you see for technology leaders in ensuring AI Agents become a democratizing force rather than another layer of digital divide?